"Screw it " Project
Screw Classification Directory
174:/media/harddrive1/SGAO/cstor-projects/screw-it
note
Need to dive down to "Dropout", "Xavier" and "SOFTMAX" loss.
Data Augmentation (数据增强)
AlexNet (7 layers) has a total number of 60 million parameters. ImageNet has a total of 15 million high-resolution images. Therefore there is a good chance that the network overfit the dataset.
Data augmentation is one approach to address such issue.
- rotating
- cropping
- add gaussian noise
- fancy PCA
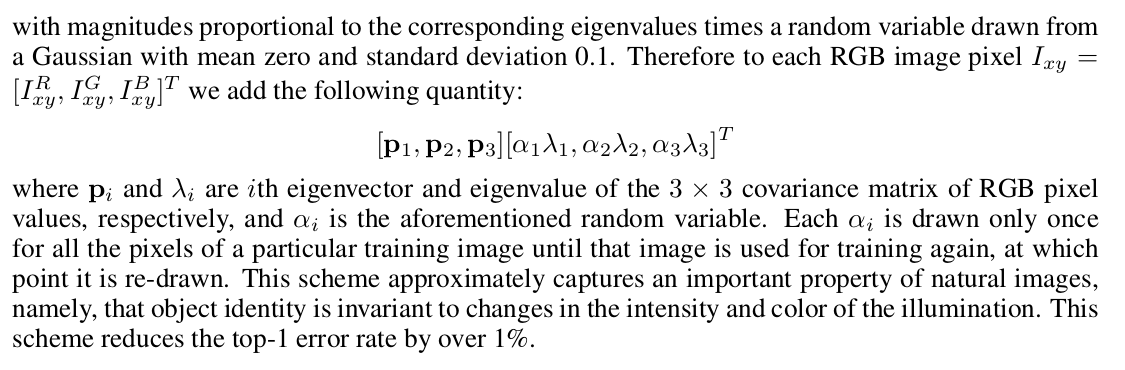
Fancy PCA
PCA color augmentation achieves data augmentation by altering the color balance of the image, i.e. adjusting the values of red, green and blue pixels in the image.
To be specific, the technique is designed to shift those values on which values are the most present in the image. Image with heavy red values and minimal green values will have their red values altered the most through fancy PCA.
Classification Model Training
Classify screws into two classes -- tight and loose.
Dataset: 38,650 for training, 4560 for testing (after data augmentation)
Model Training
Start from ZFNet (baseline)
accuracy = 87.37% accuracy = 89.52%Move to VGGNet (16 layers)
At first, the model won't learn. I did several things below to make it learn.
- Change parameter initialization from Gaussian to Xavier
- Increase mini batch size
- Reduce the number of convolution filters
- Reduce the number of neurons on the last two fully connected layers
accuracy = 92.55% @ fully_connected_layer_1: num_output=256,
fully_connected_layer_2: num_output=256
accuracy = 94.08% @ fully_connected_layer_1: num_output=512
fully_connected_layer_2: num_output=512
accuracy = 96.51% @ fully_connected_layer_1: num_output=512
fully_connected_layer_2: num_output=256
Faster-RCNN
A fantastic explanation here.
Breakthrough: RPN and Fast RCNN share convolutions at test-time, so that marginal cost for computing proposals is small.
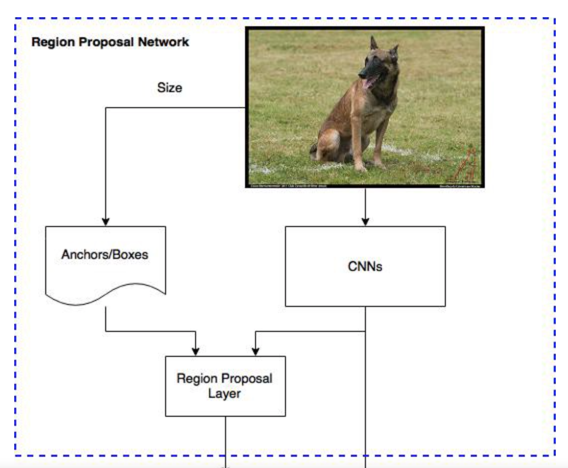
Region Proposal Network
Objective: To generate detection proposals, serves as the "attention". RPN predicts possibility of an anchor being background or foreground, and refine the anchor.
What is it: a fully convolutional network (FCN) that can be trained end-to-end
Input: feature map
Output: objects bounds, objectness scores
How training data is made
We want to label the anchors using ground-truth boxes.
The idea is that we want to label the anchors having the higher overlaps with ground-truth boxes as foreground, the ones with lower overlaps as background.
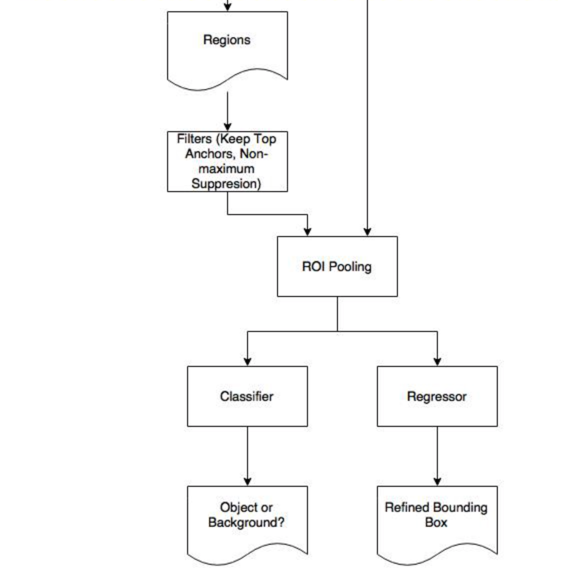
ROI Pooling
After RPN, we proposed regions with different sizes, thus different sized regions means different sized CNN feature maps.
Region of Interest Pooling can simplify the problem by reducing the feature maps into the same size.
Here is a good explanation about ROI Pooling.
- It is used for object detection tasks;
- It allows us to reuse the feature map from the convolutional network;
- It can significantly speed up both train and test time;
- It allows to train object detection systems in an end-to-end manner.
Fast RCNN
Objective: uses proposed regions to classify objects into categories and background
Training Scheme
Alternating fashion: RPN -> Fast RCNN -> RPN -> Fast RCNN
Implementation Details
- Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS)
Since RPN proposals highly overlap with each other, NMS is implemented on the proposal regions based on cls scores, i.e. objectness scores. By fixing IoU threshold at 0.7, NMS leaves use about 2,000 proposal regions per image.
RCNN (Regional Convolutional Neural Network)
One major question:
To what extent do CNN classification results on ImageNet generalize to object detection results on the PASCAL VOC Challenge?
The work was focused on two problems:
- localizing objects with a deep network
train a high-capacity model with only a small quantity of annotated detection data
The second problem actually implemented transfer learning.
Localizing Objects
The paper solves the CNN localization problem by operating within the "recognition using regions" paradigm.
Object Detection with R-CNN
The system consists of three modules:
- Region proposals: the proposals define the set of candidate detections available to our detector.
- Fixed-length feature vector extraction: extract features from each region.
- A set of class-specific linear SVMs.
Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS)
Given all scored regions in an image, for each class independently, we rejects a region if it has an intersection-over-union (IoU) overlap with a higher scoring selected region larger than a learned threshold.